Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), which is becoming more widely known as Comprehensive Genomic Profiling by Massively Parallel Sequencing (CGP), will significantly contribute to targeted therapies and precision medicine. We provide a brief snapshot of what NGS/CGP is, how it works, where it is being used, the potential difficulties and what's on the horizon.
What is Next Generation Sequencing?
- Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) is becoming more widely known as Comprehensive Genomic Profiling by Massively Parallel Sequencing (CGP)
- NGS/CGP testing will significantly contribute to targeted therapy
- Multiple genes are analysed simultaneously so there is the potential to detect all mutations in a patient specimen
- The four steps of NGS/CGP are:
- DNA extraction
- Library prep
- DNA sequencing
- Bioinformatics
- A machine reads the DNA and provides a sequence of bases. Sequences from patient samples are compared to known references
Where is NGS/CGP being incorporated?
- NGS/CGP uses the same methodology to screen for a variety of cancer genes (a panel)
- NGS/CGP is being adopted for NSCLC due to the complexity of the driver and resistance mutation tied to therapy options (Figure 1)
- NCCN and ESMO guidelines support broad molecular testing (e.g., NGS/CGP) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
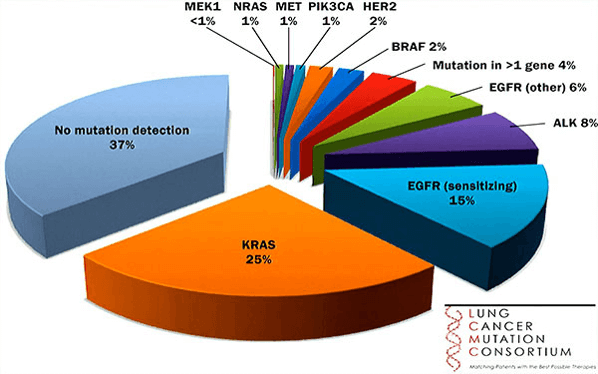
Figure 1. Mutations driving NSCLC.
What is the current situation with NGS/CGP in labs?
- There are two distinct groups of NGS/CGP panels emerging:
- Smaller, ~50 gene panels that are built with known actionable biomarkers
- Larger, 500+ gene panels to whole exome sequencing
- NGS/CGP is largely centralized to large commercial reference labs and academic institutions
- Many US labs are adopting NGS/CGP – Illumina and ThermoFisher platforms dominate the clinical space (Figure 2)
- EGFR and ALK, along with ROS1 and MET, are commonly part of lung NGS/CGP cancer panels
- Some laboratories do not include ALK in panels as they have a more cost-efficient test validated for ALK
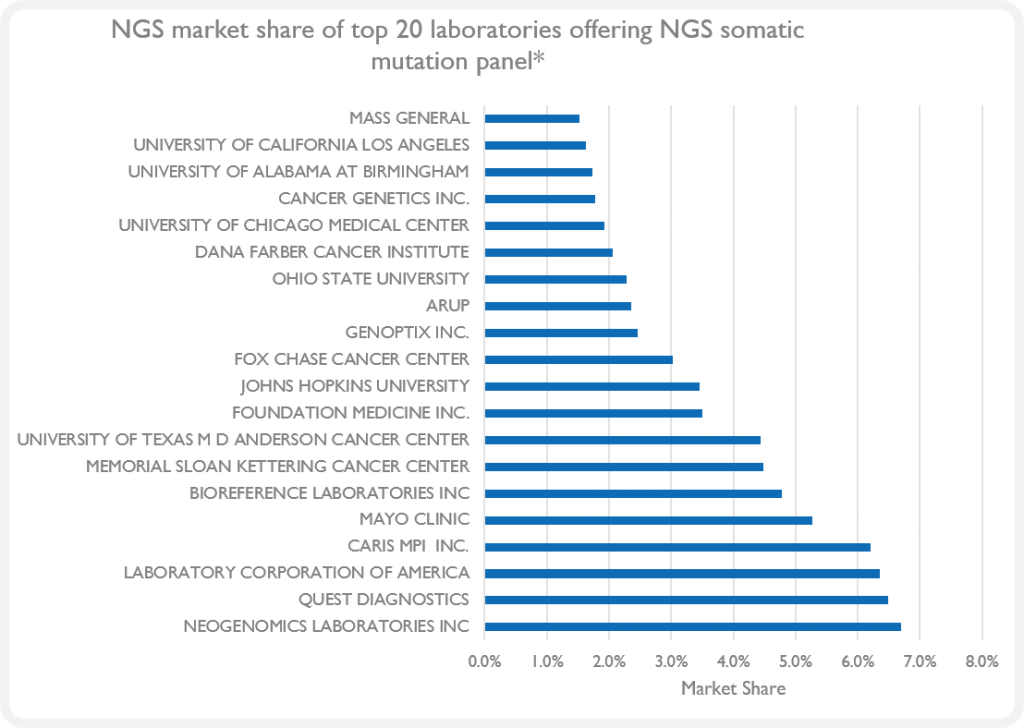
Figure 2. NGS market share of top 20 NGS somatic mutation panel offering laboratories. (*Market share is based on a blended mix of Medicare datasets of different biomarkers performed by NGS.)
Difficulties associated with NGS/CGP
- Turnaround times are lengthy as NGS/CGP is a more complex and labour intensive methodology compared with single gene tests and may exceed the therapeutic window, e.g., in AML
- NGS/CGP diffusion is currently limited to key cancer and reference labs
- Reflex strategy may be required to account for low quality or quantity of DNA
- Coverage of sequencing panels still varies between insurers and may be restricted
What’s coming up?
- The requirement for BRAF testing and sequencing of other genes in the test panel will be a major driver for the adoption of NGS/CGP
- Platform suppliers and the FDA are striving for NGS to become part of therapeutic labels
- Leading pharma and diagnostic companies will embrace NGS/CGP to address key treatment and support their own pipeline and strategic goals
